A Comprehensive Guide to Incoterms: Understanding Key Terms in International Trade
Introduction:
In the complex world of international trade, clear and precise communication between parties involved in a transaction is paramount. In this context, Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in facilitating this by serving as a common global language. These terms, developed by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), clearly and specifically define the responsibilities, obligations, and costs associated with the transportation and delivery of goods in international transactions.
Importance of Incoterms:
Utilizing Incoterms in international commercial contracts offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Ambiguity and Misunderstandings: By providing clear definitions of each party’s responsibilities and commitments, Incoterms prevent disputes and legal claims arising from misunderstandings.
- Accurate Cost Allocation: These terms clearly specify who is responsible for paying which costs, including transportation, insurance, and customs formalities.
- Risk Management: By defining the exact point at which ownership and responsibility for the goods transfer, Incoterms assist parties in managing risks associated with international trade.
- Facilitating International Trade: The use of standardized and recognized Incoterms terms streamlines and enhances the efficiency of international trade processes.
Overall, Incoterms, by clearly defining the responsibilities and obligations of each party involved in a transaction, prevent potential disputes and problems. By using Incoterms, both parties to a transaction can be assured that they are fully aware of the specific terms and conditions and can make informed decisions about their trading arrangements.
Types of Incoterms:
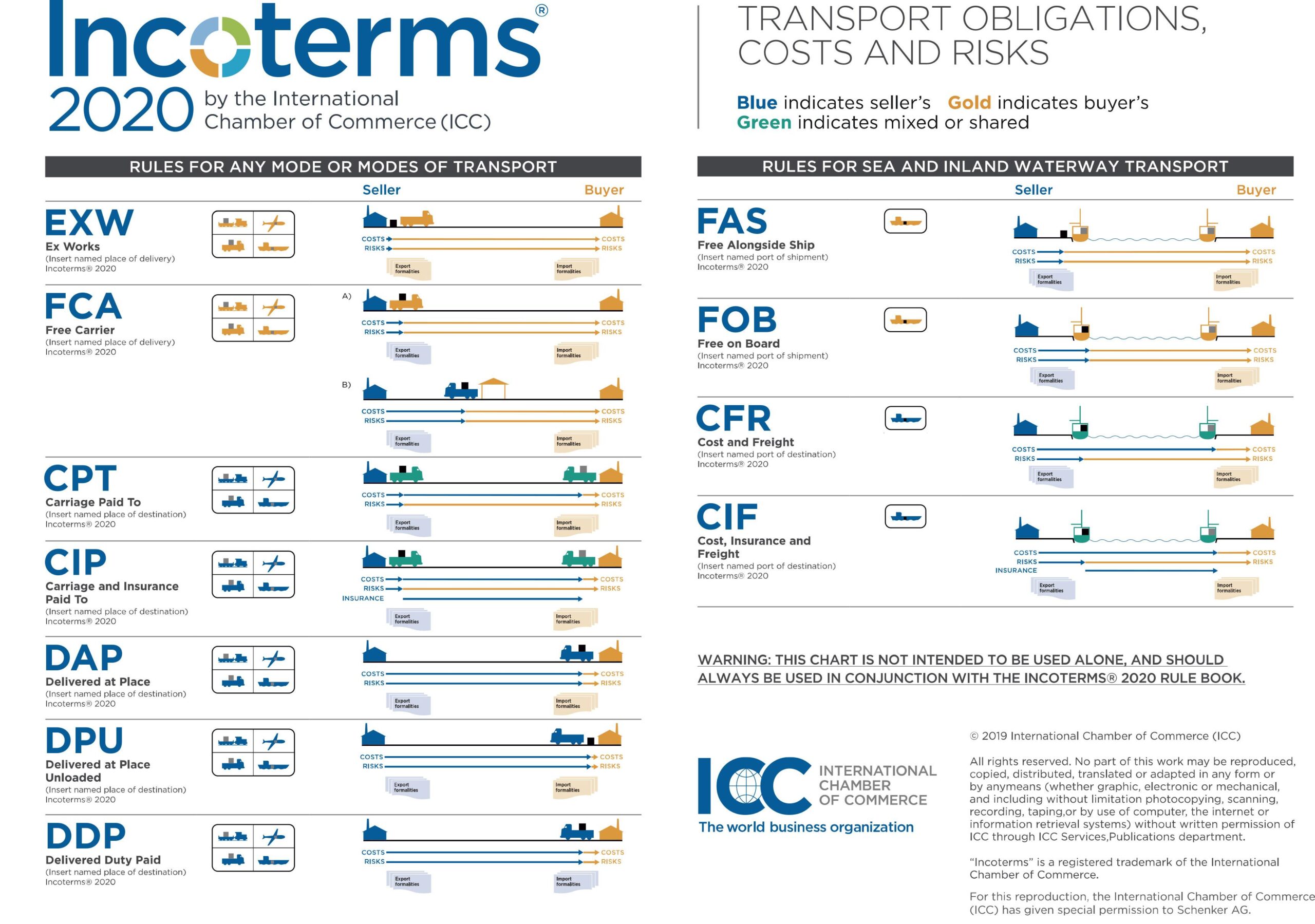
The Incoterms 2020 ruleset comprises 11 rules that are categorized into four main groups:
1) Group E (Ex Works): This group represents the simplest form of goods delivery. The seller delivers the goods to the buyer at their factory or warehouse and bears no responsibility for the transportation or insurance of the goods. The term in this group is:
- EXW (Ex Works): Delivery at the works (seller’s location)
2) Group F (Free Carrier): In this group, the seller delivers the goods to a carrier at a designated place and is responsible for the carriage of the goods to the first terminal or port. The terms in this group are:
- FCA (Free Carrier): Free Carrier at named place (carrier nominated by buyer)
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship): Free Alongside Ship at named port
- FOB (Free On Board): Free On Board at named port
3) Group C (Cost and Freight): In this group, the seller, in addition to delivering the goods to the carrier, also bears the cost of transporting the goods to the destination port. The terms in this group are:
- CFR (Cost and Freight): Cost and Freight to named port
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Carriage and Insurance Paid To named place of destination by seller
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Cost, Insurance, and Freight to named port of destination (This term was in Incoterms 2010 but has been replaced by CIP in Incoterms 2020)
- CPT (Carriage Paid To): Carriage Paid To named place of destination
4) Group D (Delivered): In this group, the seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the final place designated by the buyer. The terms in this group are:
- DAP (Delivered At Place): Delivered at Place, with customs clearance not included.
- DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded): Delivered at Place Unloaded.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Delivered Duty Paid.
Some of these terms are specific to sea and inland waterway transport and are designed specifically for situations where goods are transported by ship. These four rules are FAS, FOB, CFR, CIF.
Choosing the Right Term:
Selecting the appropriate Incoterm for each transaction depends on various factors, including the type of goods, the mode of transport, the preferences of the parties involved, and the laws and regulations of the origin and destination countries.
Key Considerations When Choosing an Incoterm:
- Consider the specific terms and requirements of your transaction.
- Carefully review the obligations and responsibilities of each Incoterm term.
- Familiarize yourself with the key Incoterm-related terms and concepts.
- Seek advice from international trade experts if necessary.
By using the appropriate Incoterm, you can conduct your international trade with greater confidence and reduced risk.
If you need assistance in selecting the appropriate term for your transaction, you can register your request for consultation on the Baramen service marketplace. Professional consultants on the Baramen platform will respond to your request. Baramen’s services are completely free on Tuesdays, and you can easily benefit from the experience and insights of professional consultants with minimal time and cost. To register a request for a trade consultation service, click on the “Request Consultation on Baramen” link. And to read more about the trade consultation service on Baramen, click on the “How to Register a Request for Trade Consultation Service on Baramen: Step-by-Step Guide” link.
The image below shows the seller and buyer’s responsibilities for each term: