Improving Supply Chain Management and Logistics: Key Strategies and Tips
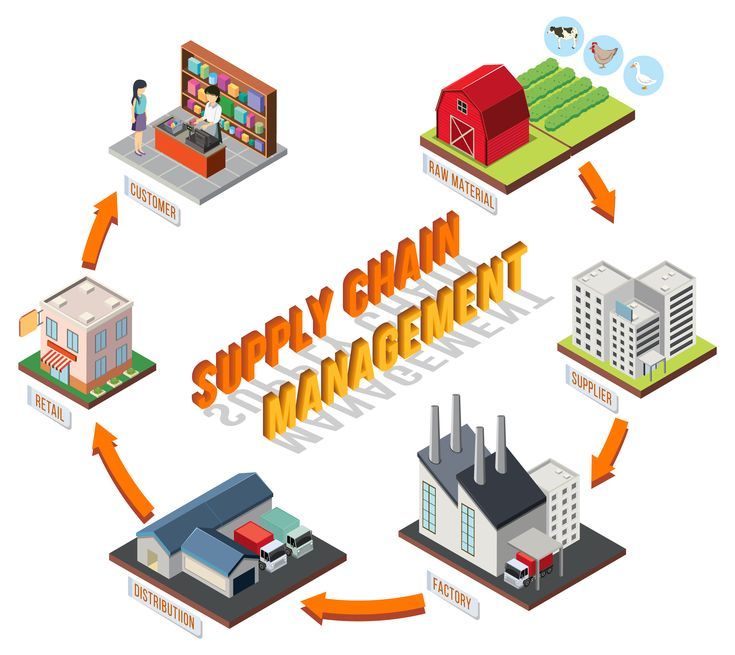
Table of Contents
Introduction
Supply chain and logistics management are among the fundamental pillars that significantly influence the success of any business. In the face of intense competition in global markets, the need to enhance performance in supply chain and logistics management has become more critical than ever. This article delves into key strategies and essential tips for optimizing and improving supply chain and logistics management.
Definition of Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the comprehensive process of planning, executing, and controlling supply chain operations. The supply chain involves all activities and processes that move a product from its initial stage as raw materials to its final delivery to the end customer.
These activities include:
- Procurement: Sourcing, purchasing, and delivering raw materials and components essential for product manufacturing.
- Production: Converting raw materials and components into the final product.
- Warehousing: Storing finished products until they are ready to be shipped to customers.
- Transportation: Moving products from the warehouse to customers.
- Distribution: Ensuring products reach the end customers.
- After-Sales Service: Providing support and services to customers post-purchase.
The primary objective of supply chain management is to enhance the efficiency and profitability of the supply chain. This goal is achieved through cost reduction, increased speed and accuracy, and improved customer satisfaction.
Importance and Benefits of Efficient Supply Chain Management
Efficient supply chain management (SCM) is pivotal for businesses, offering a plethora of compelling benefits:
Cost Reduction: Streamlining processes and minimizing waste across production, warehousing, transportation, and delivery operations leads to significant cost savings within the supply chain.
Process Acceleration: Optimized SCM and logistics management accelerates the efficiency of production, distribution, and product delivery processes, facilitating quicker business expansion and development.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Improved supply chain and logistics practices ensure prompt delivery of high-quality products to customers, thereby boosting satisfaction levels and fostering customer loyalty to your brand.
Increased Profitability: By boosting efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reducing operational costs, overall supply chain profitability can be substantially improved.
Heightened Competitive Edge: Superior SCM and logistics management empower your business to secure optimal resources and sourcing methods for raw materials, enhancing competitiveness in the marketplace.
Risk Management: Effective SCM and logistics strategies enable businesses to adeptly mitigate risks associated with raw material procurement, transportation logistics, and warehouse management, thereby fortifying operational resilience and reliability.
In conclusion, robust supply chain management and logistics are indispensable drivers of success and growth for businesses in today’s competitive landscape.
Strategies to Improve Supply Chain Management and Logistics
Effective supply chain management (SCM) and logistics are pivotal for business success, offering opportunities to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are comprehensive strategies to optimize SCM and logistics operations:
Utilize Advanced Information Technology:
- Automation and Integration: Implement robust ERP and SCM systems to automate processes, integrate data across the supply chain, and enhance visibility and control.
- AI and Machine Learning: Utilize AI and ML algorithms for demand forecasting, predictive analytics, and real-time decision-making to optimize inventory levels and streamline operations.
- IoT and RFID: Deploy IoT devices and RFID technology for real-time tracking of shipments, inventory management, and asset monitoring, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Optimize Supply Chain Processes:
- End-to-End Process Evaluation: Conduct thorough assessments of sourcing, manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and distribution processes to identify inefficiencies and streamline operations.
- Lean and Six Sigma: Implement lean principles and Six Sigma methodologies to minimize waste, improve quality, and enhance operational efficiency throughout the supply chain.
Strengthen Supplier Relationships and Collaboration:
- Supplier Collaboration: Foster strong partnerships with suppliers through transparent communication, shared goals, and collaborative planning to synchronize supply with demand and reduce lead times.
- Supplier Performance Metrics: Establish clear performance metrics and regular evaluations to ensure alignment with quality standards, delivery schedules, and cost-effectiveness.
Implement Effective Inventory Management Strategies:
- Demand-Driven Inventory: Adopt demand-driven inventory management practices such as JIT and vendor-managed inventory (VMI) to reduce carrying costs, minimize stockouts, and improve inventory turnover.
- Inventory Optimization Tools: Utilize inventory optimization tools and software to maintain optimal inventory levels based on demand forecasts, customer trends, and production schedules.
Enhance Transportation and Distribution Networks:
- Optimized Routing and Logistics: Optimize transportation routes, utilize third-party logistics providers (3PLs), and leverage economies of scale to reduce transportation costs and improve delivery reliability.
- Green Logistics Initiatives: Implement sustainable transportation practices, such as route optimization for fuel efficiency and use of eco-friendly vehicles, to minimize carbon footprint and align with environmental regulations.
Ensure Supply Chain Resilience and Risk Management:
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, geopolitical instability) and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks and maintain continuity.
- Diversification of Suppliers: Diversify supplier base geographically and strategically to reduce dependency risks and ensure a stable supply of critical materials and components.
Adopt Agile and Responsive Supply Chain Strategies:
- Agile Supply Chain Framework: Implement agile supply chain strategies to quickly adapt to changes in market demand, customer preferences, and external factors, ensuring responsiveness and competitiveness.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the supply chain team, encouraging proactive problem-solving and adoption of best practices.
Harness Data Analytics for Continuous Improvement:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage big data analytics, real-time dashboards, and business intelligence tools to gain actionable insights into supply chain performance, customer behavior, and market trends.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor KPIs regularly and use data analytics to measure performance against benchmarks, identify areas for improvement, and drive strategic decision-making.
Invest in Employee Training and Development:
- Skill Enhancement: Invest in training programs and skill development initiatives for supply chain professionals to enhance technical expertise, leadership capabilities, and cross-functional collaboration within the organization.
Collaborate with External Partners and Industry Experts:
- Industry Collaboration: Participate in industry forums, conferences, and collaborative initiatives with industry peers, experts, and academia to exchange knowledge, share best practices, and stay abreast of emerging trends and technologies.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively enhance their supply chain management and logistics capabilities, driving operational excellence, cost efficiency, and sustainable growth in competitive markets. Continual adaptation to market dynamics and technological advancements is essential for maintaining a resilient and agile supply chain ecosystem.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management and Logistics
Supply chain management and logistics encounter a multitude of challenges that can significantly impact their operational efficiency and effectiveness. These challenges include:
Complexity and Supply Chain Diversity: Managing a supply chain involves a complex network of diverse suppliers, subcontractors, raw materials, products, and multiple transportation routes. Coordinating and harmonizing these diverse elements present major challenges for supply chain and logistics managers.
Uncertainty: Supply chains are inherently vulnerable to fluctuations in demand, natural disasters, and market price volatility. These uncertainties can disrupt the smooth flow of operations within the supply chain.
Risk Management: Effective management of various risks is crucial in supply chain operations. Risks such as delivery delays, inventory shortages, transportation challenges, production and distribution complexities, quality issues, and security concerns can lead to financial implications and increased operational costs.
Supplier Relationship Management: Establishing and maintaining effective communication and collaboration with stakeholders across the supply chain—including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers—is essential but can be challenging, especially when stakeholders are geographically dispersed.
Inventory Optimization: Balancing inventory levels to avoid both excess and insufficient stock is a persistent challenge. Excess inventory increases storage costs, while insufficient inventory can lead to missed sales opportunities and customer dissatisfaction.
Raw Material Sourcing: Securing reliable and cost-effective sources of raw materials is critical for many businesses. Challenges such as price fluctuations, geopolitical instability, and concerns regarding the quality and reliability of suppliers can impact sourcing strategies.
Technology Integration: Keeping pace with technological advancements and integrating automation and information systems tailored to supply chain needs is a continual challenge. This requires ongoing investment in technology and effective management of technological resources.
Environmental Sustainability: Meeting environmental sustainability goals, such as reducing carbon footprint, managing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and preserving natural resources, presents significant challenges for supply chain managers amidst increasing regulatory pressures and stakeholder expectations.
Despite these challenges, effective supply chain management remains pivotal for enhancing organizational resilience, agility, and competitiveness. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, robust risk mitigation strategies, innovative use of technology, and collaborative partnerships across the supply chain. By overcoming these obstacles, businesses can strengthen their supply chain capabilities and achieve sustainable growth in dynamic market environments.

Conclusion
In today’s world, websites and online platforms play a crucial role in improving and optimizing supply chain management processes. These tools assist businesses of all sizes, from small enterprises to large corporations, in managing their supply chains more effectively and efficiently. This article explores key strategies for enhancing supply chain and logistics management, which not only aid in cost reduction and efficiency improvement but also help companies achieve competitive advantages in the market and attain greater success.
For further reading, it is recommended to review the article “The effect of online wholesaling platforms on supply chain.”