Warehouse Best Practices: New Methods and Technologies in Warehouse Management
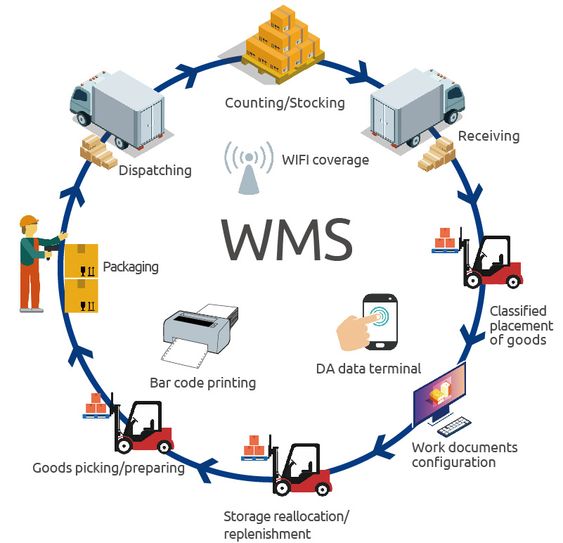
Table of Contents
Definition of warehousing
Warehousing in business refers to a set of activities and processes aimed at storing, managing, and maintaining goods and materials in a specific location. The primary goal of warehousing is to keep inventory organized and secure so it can be delivered to consumers or producers on time and in the right condition. This process includes receiving, storing, protecting, moving, and distributing goods.
A more detailed definition of warehousing includes the following:
- Receiving Goods: The process of accepting and registering goods from the manufacturer or supplier.
- Storage: Keeping goods in a warehouse in a manner that optimizes available space and allows easy access.
- Protection: Ensuring that goods are stored under suitable conditions to prevent damage, spoilage, or theft.
- Inventory Management: Monitoring and controlling inventory levels to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
- Distribution: Preparing and dispatching goods to their final destination, including packing and loading.
Warehousing plays a crucial role in the supply chain and impacts the overall efficiency and productivity of a business. Choosing the right Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and utilizing modern technologies can significantly improve performance and reduce warehousing costs.
Types of warehouses
Warehouses can be categorized based on various criteria. Here, we provide a brief overview of common warehouse classifications. It’s important to note that a single type of warehouse can fall into multiple categories.
Based on Type of Goods:
- Raw Material Warehouses: Storage for raw materials needed for production.
- Work-in-Progress Warehouses: Storage for goods in various stages of the production process.
- Finished Goods Warehouses: Storage for manufactured products ready for sale.
- Hazardous Goods Warehouses: Storage for chemicals and hazardous materials, adhering to safety standards.
- Perishable Goods Warehouses: Storage for food and products with a limited shelf life.
- Cold Storage Warehouses: Storage at low temperatures to maintain product quality.
- Controlled Environment Warehouses: Storage for goods requiring specific conditions such as temperature and humidity.
Based on Type of Operations:
- Public Warehouses: Managed by specialized companies and available for public use. Businesses can rent space as needed.
- Private Warehouses: Typically owned by a single company and used for internal needs, often by manufacturers, wholesalers, and large retailers.
- Transit Warehouses: Temporary storage for goods in transit between locations, usually located near ports, airports, and transport hubs.
- Bulk Warehouses: Storage for bulk items such as grains, liquids, and minerals, using specialized equipment for loading and unloading.
- Container Warehouses: Storage for shipping containers, typically located near ports and container terminals.
- Cold Storage Warehouses: For storing goods that require low temperatures, such as food and pharmaceuticals, using specialized temperature and humidity control equipment.
Based on Type of Ownership:
- Government Warehouses: Owned and operated by the government, typically for storing strategic goods such as food and medicine.
- Private Warehouses: Owned and operated by private entities, and can be public, private, transit, bulk, container, or cold storage warehouses.
- Rented Warehouses: Owned by one party but rented out to another individual or company.
- Shared Warehouses: Shared storage space and distribution facilities used by multiple businesses.
Special Categories
- Distribution Warehouses: Shared space for storage and distribution by multiple businesses.
- Automated Warehouses: Utilize robotic systems and automation for tasks like moving goods, shelf stacking, and order packing, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Temporary Warehouses: Used for temporary storage during special events like sports events or concerts, usually made from prefabricated structures and dismantled after the event.
- Document Warehouses: Storage for documents, files, and other administrative materials, typically featuring security and access control systems.
- Rail Warehouses: Storage for goods transported by rail, located near railway stations and using rail lines for loading and unloading.
- Dock Warehouses: For goods transported by rail, similar to rail warehouses and often located near railway stations.
- Hazardous Goods Warehouses: Storage for hazardous materials, adhering to safety and regulatory standards.
Best Warehousing Practices
"The best type of warehousing for a business depends on its specific needs and requirements."
Warehousing Practices
1) Organization and Layout:
- Proper Organization: The first step to having an efficient warehouse is proper organization and layout. This includes determining the storage location for each item, using appropriate shelving, and proper labeling.
- Optimal Layout: Design the warehouse layout to maximize space utilization while ensuring easy access to all items. Consider using vertical space and clear aisle paths for efficient movement.
2) Inventory Management:
- Accurate Inventory Control: Precise control of inventory levels is essential to avoid shortages or overstock. Inventory Management Systems (IMS) can help you track inventory levels, reorder points, and expiration dates.
- Automated Systems: Implementing an IMS can streamline inventory tracking, order processing, and reduce human error.
3) Regular Inventory Audits:
- Consistent Cycle Counts: Regular inventory audits are necessary to ensure the accuracy of inventory levels. This process involves counting all items in the warehouse and matching them with inventory records.
- Discrepancy Resolution: Address any discrepancies found during audits promptly to maintain accurate inventory records.
4) Safe and Efficient Handling:
- Safe Movement and Placement: Handling and placing items should be done in a safe and efficient manner. Using appropriate equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks can improve this process.
- Ergonomic Practices: Implement ergonomic practices to minimize the risk of injury and improve efficiency in handling tasks.
5) Shipping and Receiving:
- Streamlined Processes: Shipping and receiving processes should be designed to be fast and accurate. Using barcode scanning systems can reduce errors and speed up these processes.
- Receiving Protocols: Establish clear protocols for receiving goods, including inspection, documentation, and proper storage.
6) Inventory Management Systems (IMS):
- Real-Time Tracking: Utilize IMS for real-time tracking of inventory, setting reorder points, and monitoring expiration dates.
- Automated Alerts: Set up automated alerts for low inventory levels, pending orders, and other critical updates.
7) Regular Audits and Cycle Counts:
- Routine Checks: Perform regular audits and cycle counts to ensure inventory accuracy and prevent discrepancies.
- Record Reconciliation: Ensure that physical counts match inventory records and investigate any inconsistencies.
8) Efficient Handling and Placement:
- Safe Handling Equipment: Use forklifts, pallet jacks, and other handling equipment to move items safely and efficiently.
- Organized Storage: Ensure that items are placed in designated locations for easy retrieval and inventory management.
9) Efficient Shipping and Receiving:
- Barcode Scanning: Implement barcode scanning systems to reduce errors and speed up shipping and receiving processes.
- Organized Processes: Establish organized procedures for receiving, inspecting, documenting, and storing incoming goods.
By adopting these best practices, businesses can improve their warehousing operations, leading to enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and better customer service.
New Methods and Technologies in WMS
1)Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are among the most effective tools for improving efficiency and accuracy in warehouse operations. These systems provide up-to-date and precise information, enabling the tracking of inventory, optimizing warehouse space, and reducing the time spent searching for items. Key features of WMS include:
- Real-time Inventory Tracking: WMS allows warehouse managers to accurately track inventory levels in real-time.
- Space Optimization: By analyzing data, WMS can suggest the most efficient layout for items.
- Error Reduction: The use of automated systems for inventory recording and management reduces human errors.
- Organization and Layout: Proper organization and layout, including determining storage locations, shelving, and appropriate labeling, are crucial for efficient warehouses.
- Inventory Management: Precise control of inventory levels is essential to prevent shortages or excess stock. Inventory Management Systems (IMS) assist in tracking inventory levels, reorder points, and expiration dates.
- Stocktaking: Regular stocktaking ensures the accuracy of inventory levels by counting all items in the warehouse and reconciling them with inventory records.
- Handling and Storing Goods: Goods handling and storage should be conducted safely and efficiently, often utilizing appropriate equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks.
- Shipping and Receiving: Shipping and receiving processes should be designed to be fast and accurate. Barcode scanning systems help reduce errors and expedite these processes.
- Workforce Management: WMS can assist in planning and managing employee tasks, tracking their performance, and training them effectively.
- Data Analysis: WMS collect and analyze data related to warehouse operations, identifying opportunities for improvement in efficiency.
2) Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology RFID technology is one of the most advanced methods for identifying and tracking items in warehouses. This technology uses electronic tags and reader devices to identify items without requiring physical contact. Advantages of RFID include:
- Enhanced Tracking Accuracy: RFID provides precise information about the location and status of items.
- Faster Operation Times: RFID speeds up entry and exit processes for goods.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Manual labor for handling operations is minimized with RFID technology.
3) Robotics and Automation Robotics and automation play a vital role in increasing efficiency and speed in warehouse operations. These technologies can perform repetitive and time-consuming tasks with high accuracy. Some applications include:
- Automated Transport: Automated transport robots can move goods between different sections of the warehouse.
- Automated Picking: Automated picking systems can retrieve items from shelves and prepare them for shipment.
Smart Storage Solutions: Robots can optimize the arrangement of items and maximize warehouse space utilization.
4) Internet of Things (IoT) The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to connecting devices and objects to the internet to enable communication and data exchange between them. In warehouse management, IoT can have various applications, including:
- Monitoring Item Conditions: IoT sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions in the warehouse.
- Real-time Tracking: Internet-connected sensors can report the location of items in real-time.
- Smart Management: By analyzing collected IoT data, smarter decisions can be made regarding warehouse management.
5) Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Data analysis and Artificial Intelligence (AI) play a crucial role in improving warehouse operations. These technologies can identify patterns in data and make accurate predictions. Some applications include:
- Demand Forecasting: Historical data analysis enables the prediction of future demand and optimizes inventory.
- Route Optimization: AI algorithms can determine the best routes for item transportation.
- Error Detection: Data analysis helps in early identification and resolution of errors and potential issues.
These advanced methods and technologies are transforming warehouse management, making operations more efficient, cost-effective, and responsive to customer demands.
Benefits of Using New Methods and Technologies
- Increased Efficiency: New methods and technologies can automate tasks, reduce cycle times, and enhance process accuracy.
- Cost Reduction: These methods can help reduce costs associated with labor, warehouse space, and inventory.
- Improved Customer Service: These methods can contribute to increased order accuracy, reduced delivery times, and improved customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
“By utilizing the best warehouse management practices along with new methods and technologies, you can significantly enhance warehouse efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer service.”
Warehousing and International Trade
Warehousing plays a crucial role in international trade by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, improving customer service, managing risks, and facilitating customs processes. Optimal use of warehouses and related technologies can help companies become more competitive in the global market. Warehousing and customs are two essential components in the supply chain that closely interact with each other. Warehousing in international trade has widespread effects on the efficiency and success of the global supply chain. Close collaboration between these two sectors can facilitate trade, reduce costs, and improve supply chain efficiency. For further understanding of international trade and its regulations, it is recommended to read the article “International Trade: Laws, Processes, and Required Documents for Exporting and Importing Goods to Different Countries.“
Barameen, as a specialized trade platform, through its “Barameen Marketplace for Trade Services,” enables traders to easily connect with warehouses worldwide at every stage of their trade needs, ensuring a secure trading experience.
For more information about these services, you can explore the following links:
Sources
Inbound Logistics: https://www.inboundlogistics.com/
Material Handling & Logistics: https://www.mhlnews.com/about-us
Logistics Management: https://www.logisticsmgmt.com/
Supply Chain Management Review: https://www.scmr.com/
International Society of Supply Chain Professionals (ISCPI): https://cscmp.org/